 The global race for more innovation is rapidly accelerating – still it is lead by California. Even the east coast states like NY, Massachusetts or other US states including Texas or Florida are still looking at California when it comes to top innovation. And Europe as a whole is far back and so are most of the Asian countries.
The global race for more innovation is rapidly accelerating – still it is lead by California. Even the east coast states like NY, Massachusetts or other US states including Texas or Florida are still looking at California when it comes to top innovation. And Europe as a whole is far back and so are most of the Asian countries.
Asia the manufacturing powerhouse – not yet the innovation driver
Clearly Asia is on the run for the pole position in the world when it comes to mass manufacturing. Yet, Japan, who was actually the first Asian country with huge manufacturing power, shows a state of saturation, high prosperity and therefor high salary and its competitiveness in production leadership is slowing down. Other Asian countries have a high potential for becoming leading production farms to serve and support the growing population on earth – and with that potential a high potential for more production revenue a high potential for growing prosperity.
Strategic tech innovation still come from the US
However – in the past 30 years – it appeared that the manufacturing power is a very different economic value compared to innovation power. And while Germany, Switzerland, and France boost some of the most innovative technologies outside the US, with their “hidden champions” – it is the US who dominates the global technology space with the most relevant innovations. Relevant meaning technology that if it would be taken away would have a serious impact on the global economy.
Large corporations can’t disrupt themselves
All too often people hope that large corporations can just create an “innovation lab” in order to create innovative ideas – very much like a startup – and bring them to market. But in almost all cases that dream is bursting like a bubble after the innovation was created. When running a 20,000+ people company, each and every employee must run on 90% or better performance in order to be economically viable. If only a few would start experimenting with crazy ideas, the whole corporation me get in trouble. And if an “external” innovation lab brings a new solution into the company, the executive team quickly realizes that the sales organization has no resources to create a market or sell the product into the existing customer base, marketing has no capacity to bring new products to market, support teams are at 110% load and so forth. Corporate innovation is bound to the very same principles like a young startup: permanently under funded, lacking resources, trouble to get initial traction, difficulties building a brand and a sales force and so forth. Corporations must create very different methods and values to actually make a corporate innovation lab successful.
Government Innovation Programs
Government innovation programs have evolved and we see a huge amount of innovative solutions in many countries. However most of those innovative solutions don’t make it. Billions are pored into startups and great ideas, yet they did not return the investment. An innovation in itself is of zero value. Only of the innovation is successfully brought to market and considered a value for the customer, it begins to create a value for the owner, the participating employees and partners and the economy. Yet, a local product is never bringing a major contribution to the national prosperity. But if the product goes global, the national contribution to prosperity begins to flow. A country that is self sufficient is probably healthy and OK but never very prosper. A country with a high export rate however creates prosperity from the excess production value. A country with a high export rate from genuine and highly innovative products is the most prosper way for economic growth.
Innovation Economics – We Need To Understand
Here is probably the most interesting aspect of the innovation economics: If 5 countries are highly innovative and 10 countries not, obviously the five countries are much richer than the 10. And in the old thinking of competition, we try to be better (more innovative) then the other countries. But if all 15 countries are highly innovative, all 15 countries are rich and the five countries are richer by serving 15 rich countries than serving only 4 other rich countries and 10 poor countries. Yes, the delta is less and less but the overall economic power grows. Once we accept that model, we no longer keep countries poor or keep people dumb. Instead we keep competing but on a smaller difference. Formula-1 race cars are extremely fast and the winner wins often by a margin of a split second. Unlike 50 years ago where we saw minutes in between – simply because everything was a secret. In Silicon valley we have a spirit of sharing – even the “secret” strategies. Simply because we learned that sharing, openness and transparency is the biggest accelerator of all.
Five major initiatives for increasing national innovation
Society3 created five major initiatives to increase local innovation power and connect it to a global network to drive a global business:
1) Global Exchange
A global network where people are permanently connected. The exchange / community platform provides users instant access to all members via web, mobile and other services. The objective is to get answer on questions within a few minutes or hours, find new business partners around the globe, compare notes, and open sharing for ultra fast learning from each other.
2) Events & Meetings
While a digital global exchange is the only way to get people from around the world to collaborate and learn from each other fast, people need the personal face to face exchange too. Therefor Society3 and their local representatives conduct national entrepreneurs night events to meet and exchange on a national level and the World Innovations Forum to get together at least once a year on a global level.
3) Innovation Education & Acceleration
Education and acceleration through the accelerator program that we are currently preparing to be delivered online so everybody can participate and soon offline in the countries at local accelerators. Unique about the accelerator is the “knowledge and methods to train what it really takes to create a unique and innovative solution, build a disruptive business model, and bring it to global markets within very fast”. Society3 was named one of the top 100 most influential global accelerators.
4) Global Trading Platform
A new blockchain based trading platform will allow startups and young innovative businesses – even old ones – offer and sell their goods globally at a fraction of today’s cost – but most importantly bridging the gap from a conventional local business to a global business. Lacking the skills and bandwidth to go global is the most significant gap to today’s Silicon Valley’s leadership position.
5) Government & Corporate Innovation Labs Support
Governments and Corporations in over 100 countries are undertaking enormous initiatives to increase their innovation power. At least in the past 20 to 30 years no significant innovation stood out compared to Silicon Valley, which was an orchard just 70 years ago. The Society3 Group developed a methodical approach to accelerate significant innovation development within the respective country. Here the same techniques are applied as in the accelerator program: “Knowledge and methods what it really takes to create a unique and innovative solution, building disruptive businesses, and bring solutions to global markets within a very short period of time”.
Purpose for a global innovation push
Beyond the self serving objective to drive more business as a corporate or country, there is an additional purpose for the global innovation push. In order to eradicate hunger, poverty, and inequality, we as the human race, may want to drive “equality in prosperity” across the globe by creating innovation, entrepreneurship and business development from within the countries rather than external aid. And as a bonus we will see a wave of new innovation from all these different cultures.
![]()

 Covid-19 is only one crisis of many in our near past – and you will learn to live with crises in the future. Moreover, you should make your startup crisis resistant.
Covid-19 is only one crisis of many in our near past – and you will learn to live with crises in the future. Moreover, you should make your startup crisis resistant.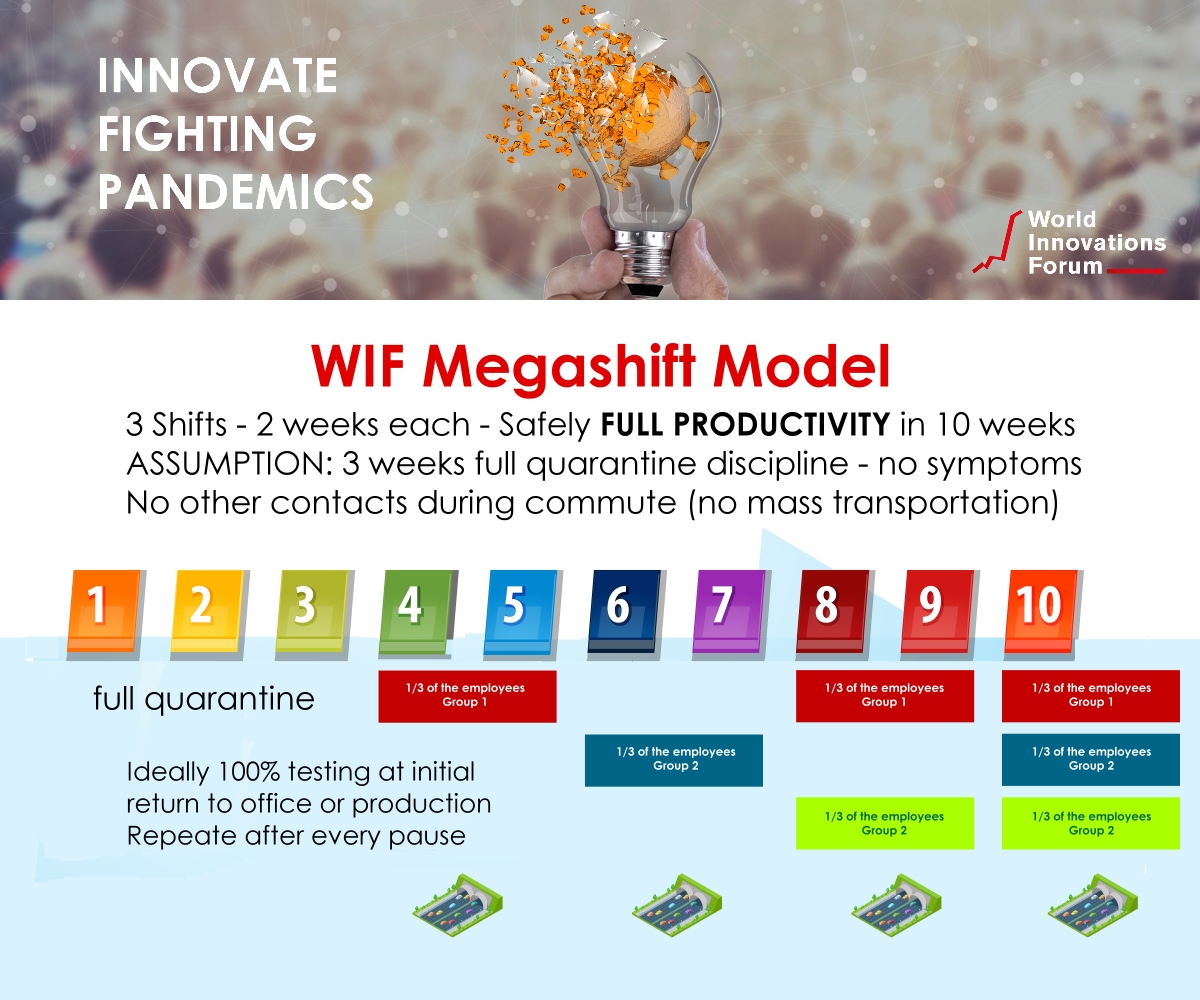



 In my previous two blog posts I shared a base view and two examples. In this post I will share some ways to get to a state of the art level of digitization in your business.
In my previous two blog posts I shared a base view and two examples. In this post I will share some ways to get to a state of the art level of digitization in your business. The global race for more innovation is rapidly accelerating – still it is lead by California. Even the east coast states like NY, Massachusetts or other US states including Texas or Florida are still looking at California when it comes to top innovation. And Europe as a whole is far back and so are most of the Asian countries.
The global race for more innovation is rapidly accelerating – still it is lead by California. Even the east coast states like NY, Massachusetts or other US states including Texas or Florida are still looking at California when it comes to top innovation. And Europe as a whole is far back and so are most of the Asian countries.